Monkeypox is a viral disease that occurs mostly in central and western Africa. It is called monkeypox because it was first identified in laboratory monkeys, while studying the effect of smallpox and smallpox vaccines on monkeys.
Transmission of monkeypox virus occurs when a person comes into contact with the virus from an animal, human, or materials contaminated with the virus. The virus enters the body through broken skin (even if not visible), respiratory tract, or the mucous membranes (eyes, nose, or mouth). The material referred to above are mainly things like clothes and bed linen.
It can spread through droplets. That is the term that the hand-washing experts at the World Health Organisation used when Covid19 started, so I would suggest that it can also spread as an aerosol. #MonkeyPoxisAirborne #CovidisAirborne.
Up until now, MonkeyPox was not thought to be very contagious but recent events are very concerning.
The virus has two different strains, a Central African (one from the DR Congo) with a CFR of 10% and a West African strain (with a CFR of 1%). The CFR in children is generally 4 to 5 time higher, so that translates to 3-6% and 30-60% for the two different variants above.
It is not clear if it can spread asymptomatically. It does have a longish incubation period so is possible.
What animals get MonkeyPox?
- Humans.
- Various animal species have been identified as susceptible to monkeypox virus. These includes rope squirrels, tree squirrels, Gambian pouched rats, dormice, non-human primates and other species.
- Other rats, mice, rabbits, and prairie dogs.
If you get scratched or bitten by one of these animals you can get MP.
What happens if you get monkeypox?
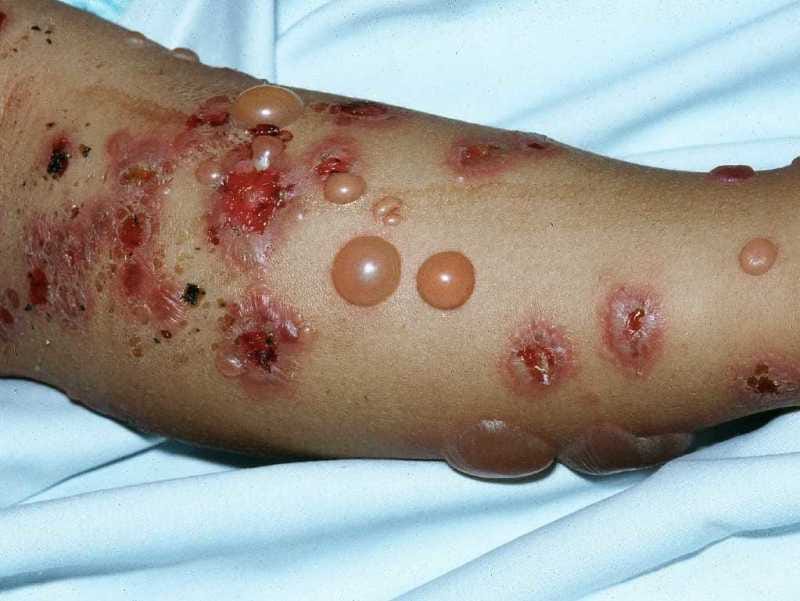
The symptoms of monkeypox are similar to but milder than smallpox. Infected people develop flu-like symptoms — fever, body aches, chills — but also swollen lymph nodes. With one to three days of the onset of fever, a distinctive rash appears, often starting on the face.


How long are you sick with the Monkeypox virus?
The incubation period of MonkeyPox (MP) is typically 6–16 days but can be up to 21.
It starts as raised spots, which turn into small blisters filled with fluid/pus. These blisters eventually form scabs which later fall off. The symptoms usually clear up in 2 to 4 weeks.
Can monkeypox be cured?
Currently, there is no proven, safe treatment for monkeypox virus infection. For purposes of controlling a monkeypox outbreak in the United States, smallpox vaccine, antivirals, and vaccinia immune globulin (VIG) can be used.
One vaccine, JYNNEOSTM (also known as Imvamune or Imvanex), has been licensed in the United States to prevent monkeypox and smallpox. Because monkeypox virus is closely related to the virus that causes smallpox, smallpox vaccine can also protect people from getting monkeypox.
Only about 10% of Australians are currently vaccinated against smallpox.
How did monkeypox start?
Monkeypox was first discovered in 1958 when two outbreaks of a pox-like disease occurred in colonies of monkeys kept for research, to test smallpox vaccines, hence the name ‘monkeypox.’ The first human case of monkeypox was recorded in 1970 in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) during a period of intensified effort to eliminate smallpox.
There are two types of the monkeypox virus
One which has a case fatality rate of about 1% and the other one with a fatality rate of about 10%. The UK outbreak outbreak appears to be the less severe type, so far.
Who does MonkeyPox affect most?
Unlike Covid19, MonkeyPox is more severe in children. As the overall CFR is about 1 to 10%, depending on the strain, it will be higher in children, just like the CFR of Covid19 is higher in the elderly. There have not been enough cases to be definitive on this.
Why has MonkeyPox recently surfaced?
There have been outbreaks in Nigeria on and off since 2017, but recently it has spread to Europe, the USA, Canada and Australia in a flash. This is very concerning.
I have speculated that it may be spreading in humans now suddenly because their immune systems have been compromised by the Covid19 vaccines. Just a thought, but before a couple of weeks ago it was considered to be a very rare viral disease and in the last 2 days it has spread into 4 continents. Global travel is a big risk as it was with Covid19.
Where has MP spread so far?
As on 20 May 2022, Monkeypox has been found in 8-9 countries:
UK (9 confirmed cases in London);
Portugal, 14 confirmed cases in Lisbon, 6 suspected:
Spain, 23 cases in Madrid;
Canary Islands (former Spanish colony);
Canada, 13 suspected cases in Quebec;
USA, I confirmed case, in Boston Mass.;
Sweden, I confirmed case in Stockholm;
Italy, 1 confirmed case in Rome;
Australia, one confirmed case in Melbourne, 1 suspected/confirmed in Sydney. .
We messed up with the SARS-CoV-2 virus by not stopping all travel quickly enough and this is why it spread around the world. #STOPTRAVEL.
Covid19 is the pandemic we never had to have. It could have been prevented at least 3 times, especially at the start.
The WHO needs to get it right this time and quickly. I doubt anyone will be signing their stupid pandemic treaty if MP22 is not contained. And I suspect it is asymptomatic and pre-symptomatic since cases have spread in Europe, North America and Australia when fevers and sickness are being closely (not that closely) because of Covid19. I also suspect it is airborne too.
Can the MonkeyPox virus mutate?
You bet it can mutate, and it may have already mutated to the variety that is spreading right now. Knowing how complacent and pathetic humans are, this could mutate into a mirage of variants in no time.
How contagious is the MonkeyPox virus?
Up until now it was thought it was not very contagious, but recent events suggest otherwise. I also highly suspect it is spread as an aerosol like Covid, and if it spreads, it will mutate to become more and more contagious.
This simulation (in article, link below) is a bit scary. I do not know how seriously to take it though, as it could be the WHO fear-mongering to get their pandemic Response Treaty that they should no get as they stuffed up Covid19.
12 responses to “Everything you need to know about the MonkeyPox virus right now.”
Granted that, there have been outbreaks of Monkeypox before, in the USA 71 cases in 2003 from a shipment of live animals, and in 2017 at a naval base in the UK, but the problem we have here is that it is already in 11 countries and 4 continents at the same time and there are 100s of cases and what concerns me is that the covid vaccinated may have compromised immune systems that may be allowing MP22 to spread, and if it spread into many more people, it might mutate into another variants, if that has not happened already.
[…] Everything you need to know about the MonkeyPox virus right now. […]
Monkeypox is not supposed to be very contagious but yesterday it was 12 countries and 4 continents. Now it is like 15/16 countries and 5 continents.
https://www.devdiscourse.com/article/health/2046909-argentina-reports-first-suspected-case-of-monkeypox?fbclid=IwAR3_qFeCz_KRtKXrLc9We6LNhjC67SK1C_WjDyaTcyoaWdBi4WnRzOdvVVA
also reported in Israel, Germany, Switzerland and Austria now
https://twitter.com/islandofcovid/status/1528275343999741954?t=53p4TJUMwQqVwKpwvN3h-w&s=07&fbclid=IwAR3v438GPviHEHikRPssqgNNK2h673rmDT2s80mi-JgEQ0vgapBDj-ZzORE
belgium introduces 21 days quarantine
https://www.dailymail.co.uk/news/article-10841885/Doctors-warn-significant-rise-UK-monkeypox-cases-surge-two-three-weeks.html
Monkeypox is a DNA virus (has a double helix structure).
Here is a quick lesson in virology of poxviruses.
https://twitter.com/cggbamford/status/1528385454617272322?t=PsKvJcidFpMBFpHOVZe1Eg&s=07&fbclid=IwAR3BXJ7DexQ47_L0b00FLd_qffIZa_5MH9gscGheJT1p5HDoTzGC58QYplE
This is what Dr Robert Malone thinks about #monkeypox, but I wonder if the covid vaccine may have altered the immune system of humans to make them more susceptible. It is spreading rather fast for my liking and the incubation period is longer than covid.
Interesting it is a DNA (double helix virus) so it will not be able to mutate as much as SARS-CoV2.
For your reading. I save my judgement for a few weeks.
https://rwmalonemd.substack.com/p/monkey-pox?s=r&utm_campaign=post&utm_medium=web&utm_source=direct&fbclid=IwAR3vHR2GloyWXWSqYfyVwr1lozDRLDY61GKKpj8bdQP1SMt352jePohKA5o
Scientists are now thinking the monkeypox currently in europe may be a mutation of the previously known monkeypox and it may mutate faster for a double helix DNA virus, and hypermutate the more it spreads.
More here:
https://twitter.com/EnemyInAState/status/1528833592532541443
[…] Everything you need to know about the MonkeyPox virus right now. […]
[…] deaths from monkeypox reported. 5 dead ?? Everything you need to know about the MonkeyPox virus right now. “Monkeypox” virus outbreak in the UK (and Nigeria) 7 in UK, 8 in […]
[…] Everything you need to know about the MonkeyPox virus right now. […]